Making Trinidad and Tobago a FinTech-Enabled Hub
A well-developed well-driven FinTech or financial technology ecosystem has the potential to bring increased diversity and advances to the financial sector of Trinidad and Tobago. The financial sector has consistently been one of the five highest contributors to the country’s GDP, adding US$1.8 billion to earnings in 2018 (Ministry of Finance Review of the Economy 2019). This sector is characterised by a solid banking faction, excess liquidity, low levels of systemic risk build-up, and a large capital base with Stock Exchange Market Capitalisation of over US$20 billion and Commercial Bank assets of over US$21 billion (Central Bank of Trinidad and Tobago Financial Stability Report 2018; Ministry of Finance Review of the Economy 2019).
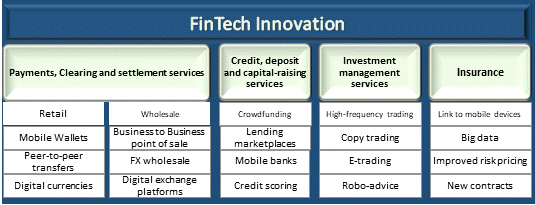
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) defines FinTech as “technologically enabled financial innovation that could result in new business models, applications, processes, or products with an associated material effect on financial markets and institutions, and the provision of financial services.” The term FinTech is generally associated with digital banking and payment systems but covers many other broad areas including credit, deposit, and capital-raising services, investment management services, and insurance (Thakor 2019). FinTech is revolutionising the financial sector and leveraging innovations like artificial intelligence, robotics and blockchain, to drive financial service innovation with ground-breaking technology solutions such as crowdfunding, peer-to-peer transfers, and robo-advisory services (refer to Figure 1).
Figure 1 Technology-enabled innovation within the financial service sectors
The FinTech industry has been gaining strength throughout the Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) region with more than 700 platforms that currently offer financial solutions based on new technologies. Tobias Adrian, Financial Counsellor and Director of the Monetary and Capital Markets Department of the IMF has stated that every country, including the countries of the Caribbean, would be wise to prepare and embrace the FinTech revolution, in the hope of realising its far-reaching social and economic benefits despite the challenge of balancing between enabling financial innovation and addressing financial integrity, consumer protection, and financial stability. A thriving FinTech ecosystem has been commended for improving tax collection, promoting financial inclusion, increasing accountability, increasing transparency and security, and improving efficiency, employment, foreign direct investment, foreign exchange earning potential, and economic growth (OECD 2019; Lund, White, and Lamb 2017; Manyika, Lund, Singer, White, and Berry 2016; Manzali de Sá-Kaye 2020). In addition, regulators in many countries have accepted the fact that regulation is crucial for the development of their FinTech ecosystem so that FinTech can deliver its benefits while maintaining financial stability.
On this backdrop, the TTIFC is also focused on the creation and development of a FinTech Hub in Trinidad and Tobago as one of its mandates is to drive the adoption of cashless transactions and financial inclusion within the society, making the country a FinTech-enabled Hub of the region.
This can be done using all of or a combination of ways, including upskilling of the workforce, having public policy discussions, legislative changes, incentives for FinTech, the creation of an innovation hub and sandbox.
Key Initiatives
The TTIFC’s Approach to making Trinidad and Tobago a FinTech Enabled Hub
 FinTech Readiness Assessment to help understand where Trinidad and Tobago is with regards to manpower, infrastructure, legislative environment, needs of FinTech firms.
FinTech Readiness Assessment to help understand where Trinidad and Tobago is with regards to manpower, infrastructure, legislative environment, needs of FinTech firms.- Innovation Hub to ready the workforce, local FinTech companies, and attract foreign FinTechs through accelerator and incubation programmes, funding, and training.
- The roadmap will guide the sequencing, timeline, and processes, for advancing the development of the hub. This will include the implementation of policy and legislation, the use of sandbox to test new products, attracting foreign FinTech, and ultimately becoming a FinTech Hub.
